How to Create a Front End for a MySQL Database in 4 Steps
How to Create a Front End for a MySQL Database in Five: Complete Guide with Expert Tips
You are about to embark on a new application development project: the application requirements are clear. The entity relationship diagram (ERD) and the database schema are ready.
It is time to start developing.
But hold on: though the back-end data structure is clear, you dread how slow and painful it will be to build a bespoke front end on top of your back end. There’s got to be a better way to build a front end than spending hours wrestling with React UI component libraries.
And there is.
If you are a back-end or full-stack application developer, a database programmer or administrator, or even a business analyst with a strong grasp of SQL, this article is for you.
In it, we will explain how to create a web front end for a MySQL database using Five.
Goals & Outcomes: Creating a Front End for a MySQL Database in 4 Steps
In this how-to guide, we will go through the 4 steps of creating a front end for a MySQL database. These steps are:
- Creating a new application with Five.
- Creating a MySQL database with Five.
This is where we create the tables and fields of our MySQL database and assign data and display types. - Creating forms with Five.
For the sake of simplicity, the only front-end components we are building in this tutorial are forms to give our end-users the ability to read, write, update, or delete (CRUD) data contained in our MySQL database. - Launching the application.
We will deploy the application locally and free of charge using Five’s free trial.
As a result, we will get a custom MySQL database with fields, as well as a front-end or graphical user interface (GUI) for end-users to interact with our MySQL database.
If you’d like to skip ahead to our “How To” section, simply scroll down to “How To Create a Front End for a MySQL Database In 4 Steps.“
What Is Five?
Five is a low-code development environment that helps software developers build and deploy custom business applications faster. It provides developers with pre-built components that can be mixed with full code almost anywhere.
The Five Integrated Development Environment (IDE) covers the entire full-stack application development process, from data modeling to application deployment. It is ideally suited for building business applications for internal or external users.
Typical applications built with Five are internal tools, departmental applications, operations software, business partner portals, or B2B applications. Good examples are custom CRM solutions, custom membership systems, custom order management systems (OMS), custom product information management systems (PIM), or custom inventory systems. Check out our use cases for application templates and inspiration.
Developers can access Five’s trial to develop and test applications. There is also a free download available to test applications locally. A subscription to Five is required only if an application is ready for end-users.
Start-ups to large businesses can all rely on Five as their all-in-one development environment to develop, maintain, and deploy custom business applications in a rapid and standardized manner.
What Is Five’s Tech Stack?
A tech stack (or software stack) describes the combination of technologies used to build an application.
Popular stacks that are known for their ability to produce fast and powerful web applications are:
- MERN: MongoDB, Express, React, and Node.
- LAMP: Linux, Apache, MySQL, PHP/Perl/Python.
- MEAN: MongoDB, Express, Angular, and Node.
- For a comparison, check out our blog post on MEAN vs MERN here.
Each stack is named after the core technologies that make up the stack, from the web server to the database (MongoDB or MySQL) to the programming language used for the front-end and back-end development.
In recent years, end-to-end JavaScript stacks such as MERN or MEAN have grown in popularity. The only difference between the MERN and MEAN stack is the choice of front-end framework (React or Angular). But even the older LAMP stack is still a popular choice due to its combination of tried-and-tested open-source technologies with great support communities.
How does Five compare to these popular software stacks?

Five gives developers everything they need to develop a cloud-native, modern full-stack web application in one platform.
Applications that are built with Five
- use a MySQL database,
- are extensible through SQL, JavaScript and TypeScript,
- use the popular React component library Material-UI for their auto-generated front end, and
- can be deployed in a single click to a highly scalable infrastructure as a containerized web application (using Docker & Kubernetes). Applications built with Five run in the cloud using AWS EKS (Elastic Kubernetes Service).
Why Use Five, Instead of an Open-Source Software Stack?
Why should developers use Five, instead of MEAN, MERN, or LAMP to build web applications?
The answer is faster development speed, higher standardization, and ease of use.
Of course, developers can always select to develop applications in the traditional, full-code way, setting up their environment and starting from there. This has always been and will always remain a valid choice for application development.
But there are at least three advantages when using the Five IDE:
- Developers can get started with building the application right away, and don’t have to waste valuable time setting up their software stack. This contributes to a faster speed of development.
- Developers don’t need to be familiar with all the latest technologies and tools required to build & deploy a full-stack application.
Inside Five, they find everything they need to build, maintain, and deploy an application to the cloud, without ever having to leave the Five development environment. For example, there is no need to create a SQL script in a MySQL GUI external to Five, sift through component libraries, or figure out the AWS management console for cloud deployment. All of this is covered by Five, accelerating the delivery of cloud applications to end-users. And Five is extensible through full code written in SQL (queries), JavaScript, or TypeScript (for functions and processes). Five also supports popular technologies such as webhooks or APIs. - Last, Five makes it easy for back-end developers to create a frontend, or for front-end developers to create a backend, even if they are not experts in the usual tools used to create a frontend or backend. And developers of all stripes – frontend, backend of full-stack – can easily launch applications to the cloud, even if they do not have cloud expertise. This makes Five very easy to use and get started with.
With Five, developers get access to an all-in-one developer tool that goes beyond a traditional IDE. Now, let’s understand how to create a front-end for a MySQL database with Five.
There are four steps involved to create a front end for a MySQL database:
- Creating a new application with Five.
- Creating a MySQL database with Five.
- Creating forms with Five.
- Launching the application.
How to Create a Front End for a MySQL Database in 4 Steps
Creating a New Application With Five
Let’s start by creating a new application with Five. To do so, access Five’s free trial. The first screen you will see looks like this.
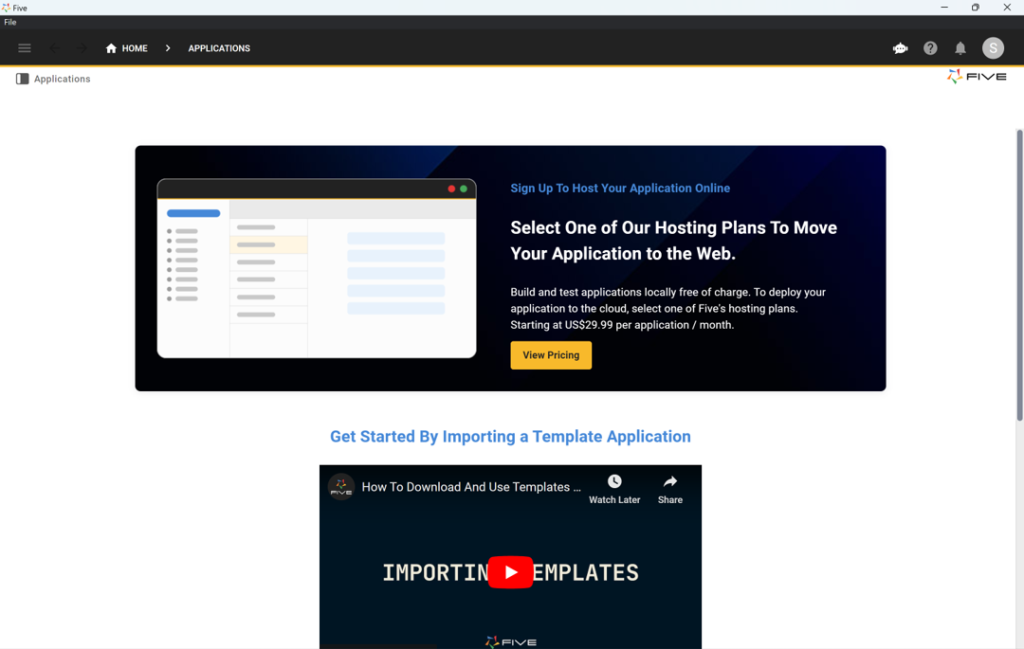
Here’s how to create a new web application using Five:
- Start by clicking on Applications in the top left corner.
- Next, click on the yellow Plus button.
- Give your application a descriptive name in the Title field, and save it by clicking the tick mark in the top right.
- Done: You have successfully created your first application in Five.
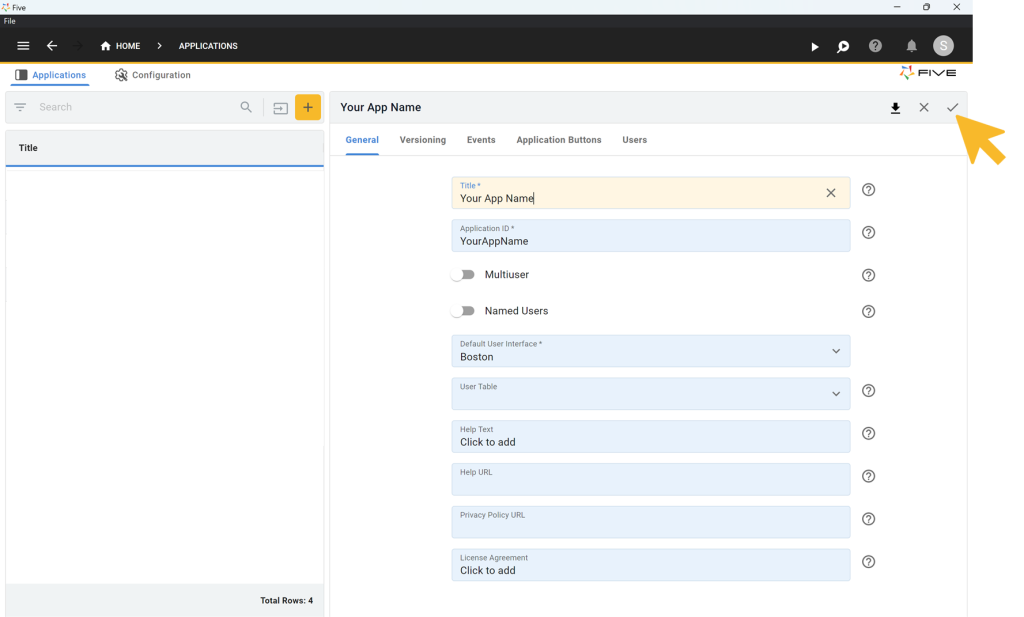
You will now see your new application in the list of all applications that you have created with Five.
Next, click on the blue “Manage” button that has appeared in the top right corner to access all of Five’s development features.
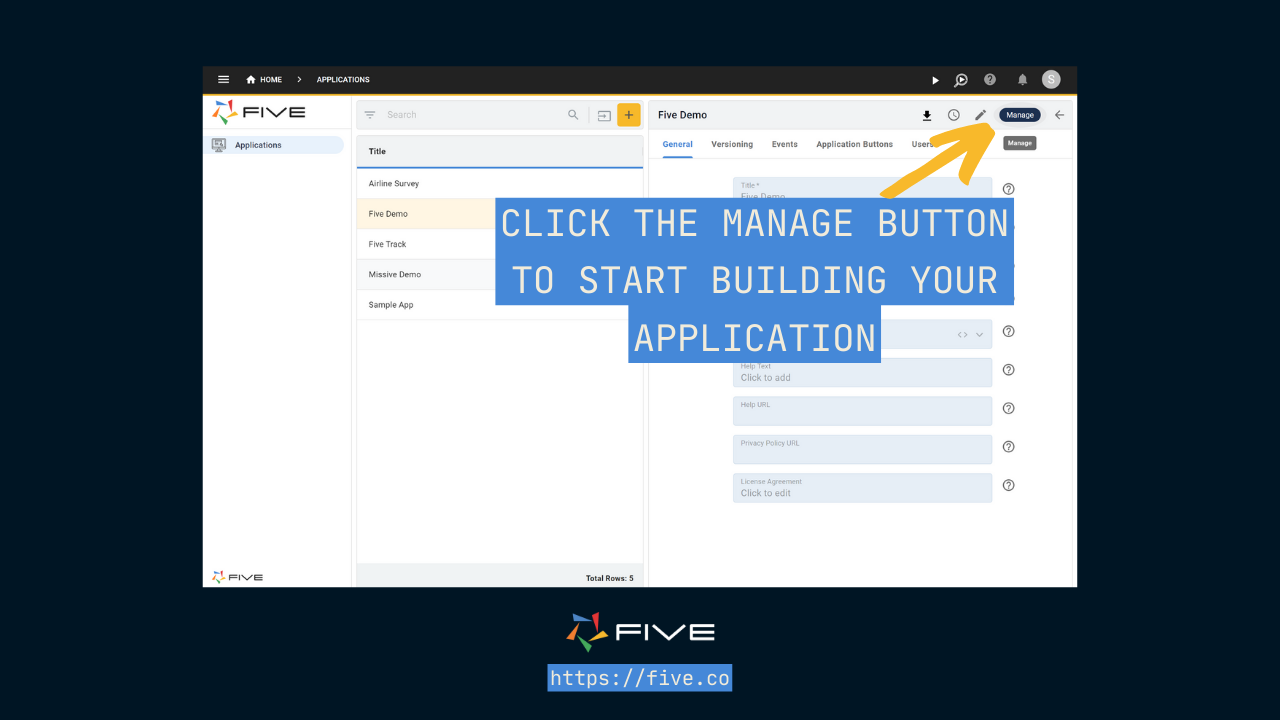
EXPERT TIP: Don’t spend too much time on all the other application settings just yet.
There is a lot that you can customize for each application, from making it a multi-user application, to configuring application logs, or customizing application buttons. For now, let’s simply leave the default choices as is. By having created a new application, we have access to all we need to start creating our front end for a MySQL database.
Creating a MySQL Database With Five
Next, we create our MySQL database inside Five.
Applications built with Five use an integrated MySQL database. The database can be created and managed straight from inside the Five development environment. No external MySQL GUI, such as dbForge Studio, phpMyAdmin, MySQL Workbench, Navicat for MySQL, DBeaver, or Beekeeper Studio is required to create, alter or update tables.
However, if you are not ready yet to abandon your MySQL GUI for something new yet, you can also simply import a SQL dump straight into Five. Once imported, you will find all your database tables, their fields, display types, and stored procedures inside of Five. For instructions on how to do so, visit our documentation on help.five.org.
In this tutorial, we will use Five to create fresh MySQL database tables. To do so, click on Manage, and then on Data, and on Table Wizard.
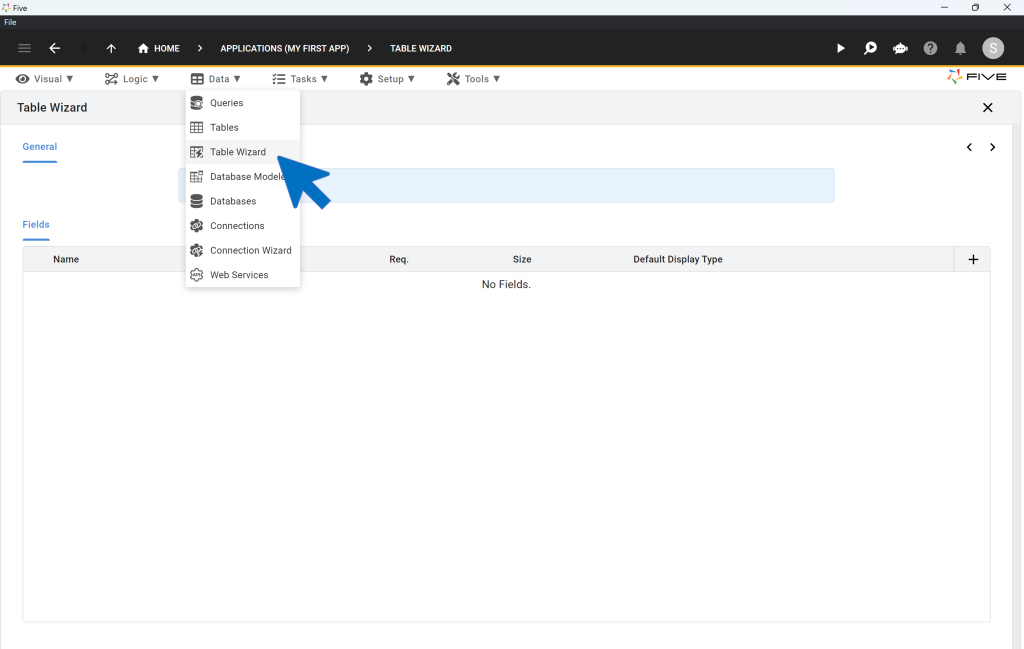
Using the Table Wizard, you can:
- Create new database tables from scratch,
- Assign data and display types to your database fields, which define how data is stored and displayed to your end users,
- Build relationships between tables using Primary Keys and Foreign Keys,
- Import CSV files straight into your database tables, and
- Add new fields to existing database tables.
Simply add new fields to your table by clicking on the Plus icon. Define their data and display types, as well as their size, and you’re done creating a database table.
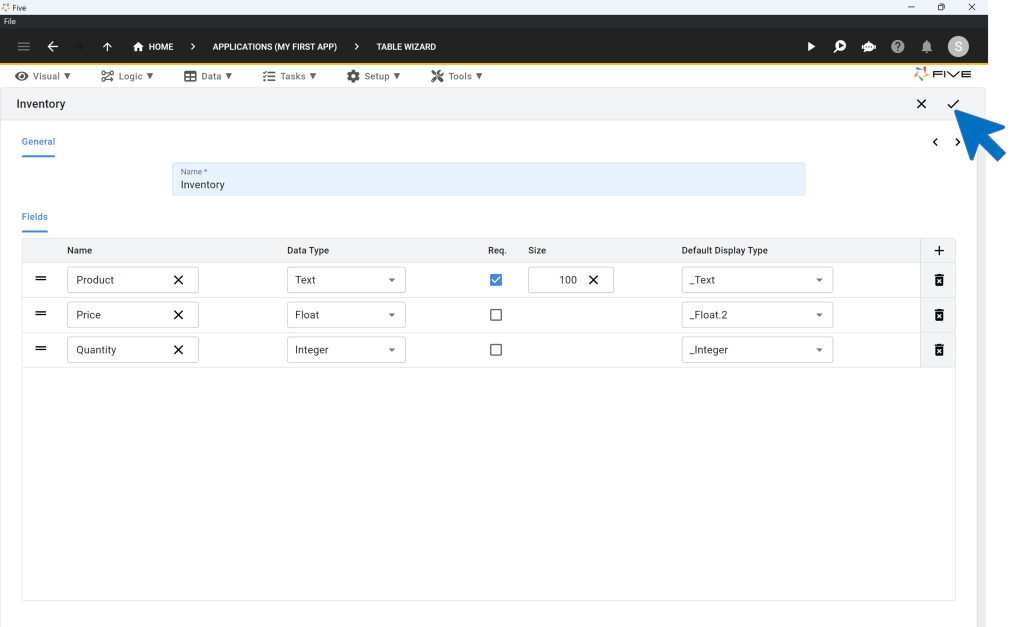
For a quick tutorial on how to create your first database table, follow our Quick Start Guide that walks you through setting up database tables, as well as building relationships between them.
Or watch this YouTube video that explains Five’s Table Wizard:
EXPERT TIP: Five automatically creates Primary Keys, and Foreign Key fields when you establish a relationship with another table, for you. This means that when you create a new table from scratch and inspect its fields, you will find that Five has automatically added an additional field, the Primary Key, to your table. The field is always named “TableNameKey” and is stored as a GUID. This is where Five stores primary keys for you. So there’s no need for you to create a separate field to serve as a primary key.
To view keys, click on Data and then Database Modeler. The database modeler visualizes your database schema for you and shows you all of your tables and their relationships.
Creating Forms With Five
Once your database tables are set up, you can start creating forms. Simply click on Visual, and then Form Wizard in the Menu on the top.
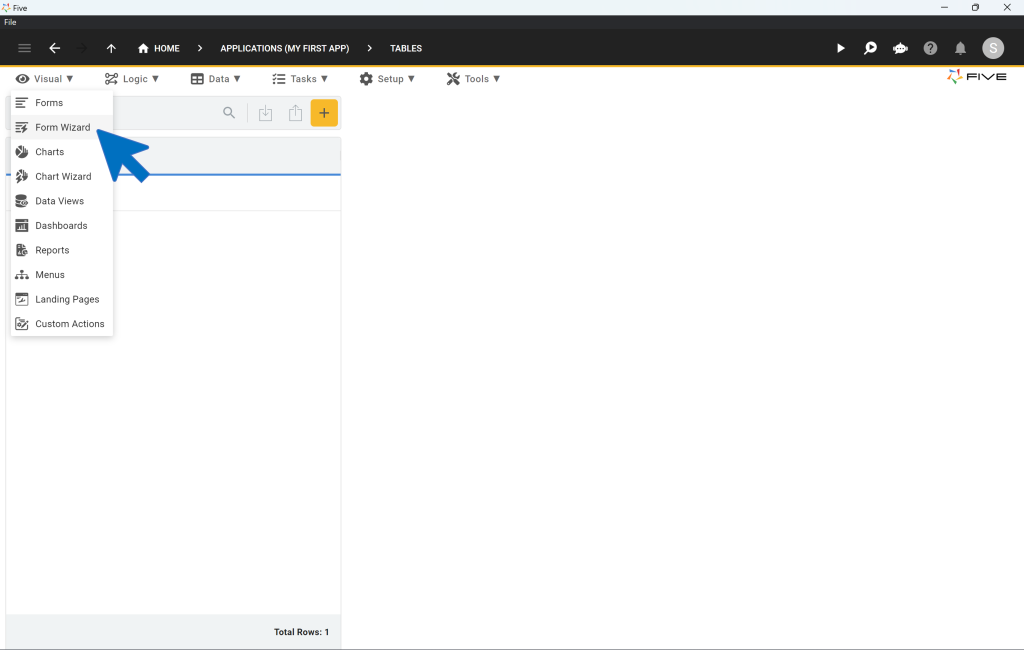
Inside the Form Wizard, select the database table that your new form will be pointing to.
For example: say your database contains a table called “Inventory”. The form wizard will let you select this table, and will automatically create all the fields that your form should contain for end-users to interact with your database table.
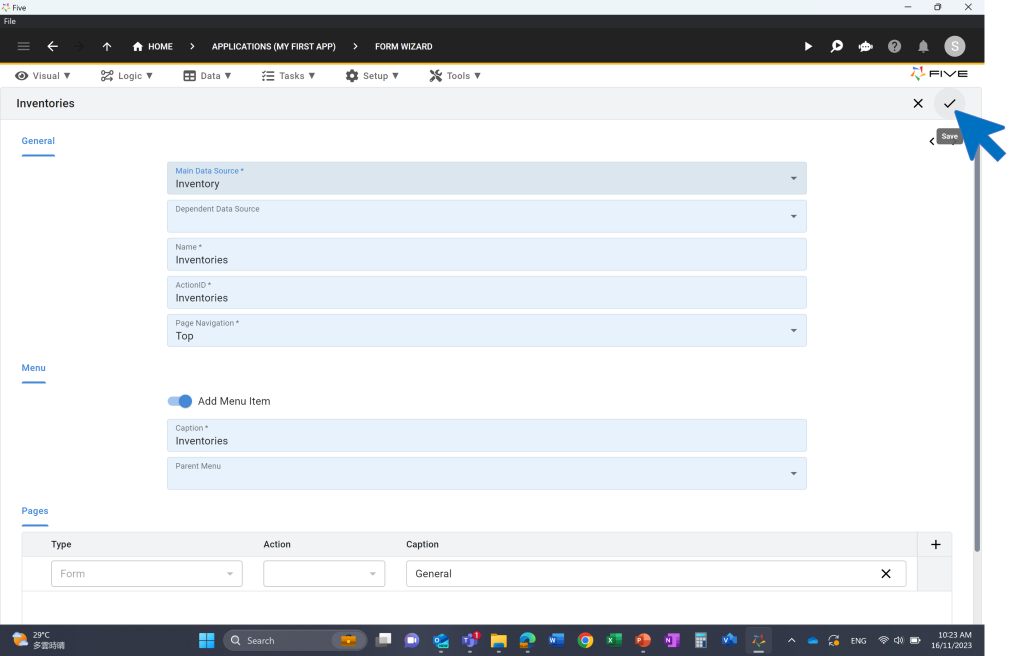
Going from database table to form usually takes just a few seconds. Five makes it incredibly easy to build a CRUD application through its tight integration of the MySQL database into the overall development process. Simply follow this video to create your first form:
There are also plenty of customization options that Five gives you for forms. We will not go into all of these now, so here is just a quick list:
- You can adjust the size and order of your form fields.
- Through the use of “Show If”, “Read Only If” or “Required If” and JavaScript conditions, you can create forms with conditional logic.
- You can create custom display types, or apply regular expressions (RegEx) to validate the data that end-users store inside of forms.
- You can assign events to end users’ actions on forms. For example, you can run a JavaScript function that is tied to an “on enter” or “on exit” event in relation to a form field.
In a nutshell, there is little that you cannot do with a form built inside of Five. But if you still have questions, then our user community is a good place to learn more about Five’s features.
EXPERT TIP: Forms can get pretty complex. It’s best to start with a bare-bones form and delve deeper into the customization options later.
The form might not look pretty at the start, but it does what it is supposed to do: it lets end users interact with your database through a graphical user interface. Later on, you can customize forms based on your requirements.
Launching The Application
We have now completed all steps to create a single table, single form application with Five.
But let’s remember what we are here for. we want to learn how to create a front end for a MySQL database. But wait: we are almost at the end of the tutorial, and haven’t done anything with regard to the user interface or frontend design yet. Well, you don’t have to. Five creates it for you!
To better understand this, let’s launch our application for the first time. Click the “Run” button in the top-right corner. Your application will open and you can preview your application in a new tab.
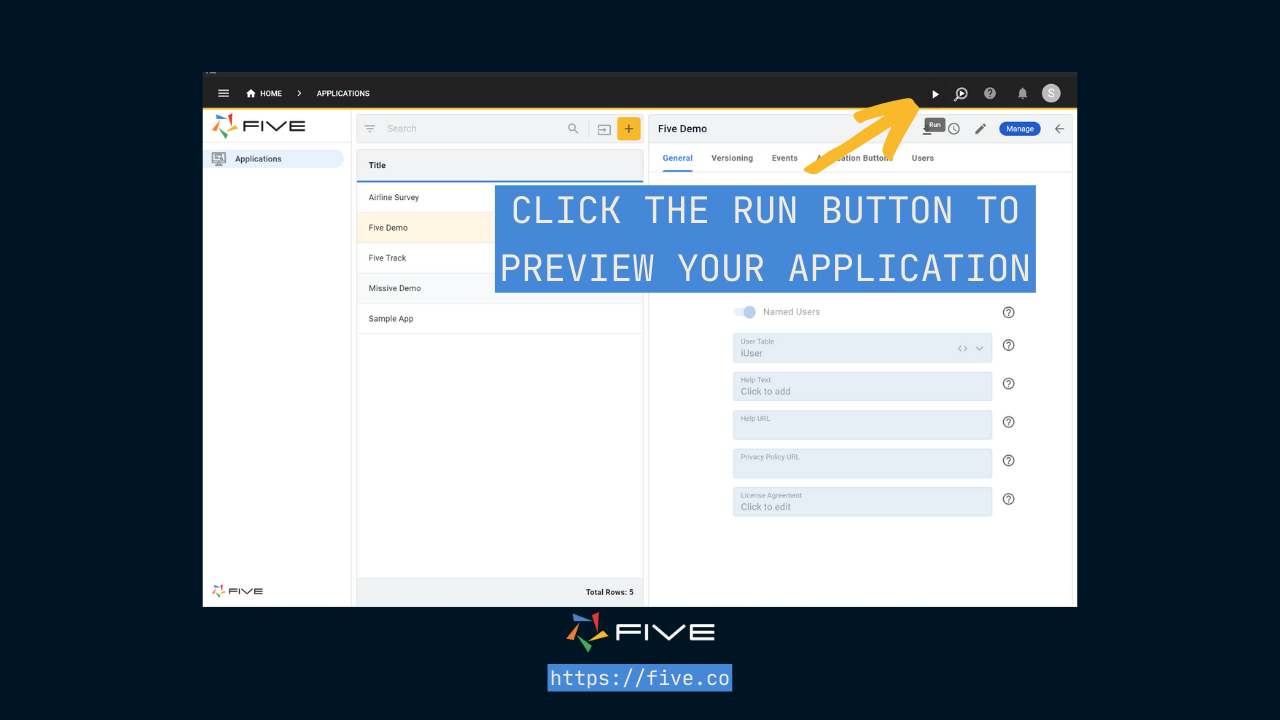
Five automatically creates a clean and intuitive admin panel user interface on top of your MySQL database for you. Running along the top and the left-hand side, Five gives you a menu that lets end-users navigate through your application. On the top, you have icons for in-app help or a user avatar that is particularly handy for multi-user applications. And in the center, there is a main area for your users to interact with your application, its forms, charts, dashboards, or any other element that you decide to develop for them.
This user interface is customizable through themes, buttons, or custom front-end components. It also handles more complex data structures very well, by letting you add pages, drill downs, or parent-child menus.
EXPERT TIP: If you are building your application locally, you can only deploy the application into your development environment. When using Five on the cloud (with a paid subscription), Five gives developers a development, testing, and production environment for each application and application instance. This makes managing releases across development, testing (QA), and business teams very easy, as developers do not need to worry about setting up and maintaining these environments manually.
Understanding The User Interface
Let’s delve a bit deeper into the user interface that Five provides you with.
Five’s user interface for end-user applications is primarily made for data-driven, multi-user business applications. These business applications can range from tools purely used by internal staff to business partner or supplier portals to custom CRM or OMS systems. Through the user interface, the end-user can store, amend, view, visualize, report, or query data.
Five comes with dozens of popular UI components for displaying data, from ratings to date pickers to radio buttons. Five’s UI can also be extended via form-style plugins.
The user interface is responsive and automatically adjusts to a smaller screen size. It renders well on all common devices, from mobile phones to desktops.
EXPERT TIP: Even though Five’s UI is responsive by default, developers should carefully think through their end users’ experience.
For example, Five lets developers define a custom grid for dashboards, by defining a custom grid of columns and rows. For mobile, it’s best to keep the number of columns and rows to a minimum, as end-users typically cannot consume too many visualizations at once on a small screen.
The notification icon in the top right corner is fully programmable and can be used to send notifications to end-users, based on their user profile. Developers can also add more (custom) buttons in the application bar on the top.
Overall, the user interface is designed to give developers maximum speed in their application development, without making sacrifices to the overall end-user experience.
Conclusion & Next Steps
In this article, we covered how to create a front end for a MySQL database. We used Five, a low-code development environment designed for use by experienced software developers, to do so. Five is best used for building custom business applications. It makes the process of creating a front end on a MySQL database quick, easy and efficient and provides developers with a pre-built user interface.
Now that you have learned how to create a front end for a MySQL database, where should you take your application next? So far, we only covered the basics of Five. To continue developing your application why not try:
- Making it a multi-user application and creating different access rights and permissions for different user groups?
- Adding a mail merge to notify users about changes inside your application?
- Writing a SQL query inside Five to create reports, charts or dashboards?
- Adding JavaScript functions to connect Five to external systems, such as Slack?
Expansion: Build a Web App on a MySQL Database
Learn how to build an entire web app on a SQL database by following our step-by-step app development guide.
The guide starts with the creation of a database from scratch and finishes with a web app that contains a chart, PDF reports, and forms for users to interact with your data. You will learn how to combine all these front-end elements with your back-end database.
Best of all: it’s free to follow!


