5 Real-Life Database Examples (With Templates You Can Use Today)
Discover the Everyday Value of Databases: 5 Real-Life Examples Explained
Almost every business or organization uses a database, whether for managing customers, tracking inventory, or analyzing financial performance. Despite their widespread use, the concept of a database can seem abstract or overly technical to those without a technical background. This can make it challenging to understand how databases add value to day-to-day operations.
To bridge this gap, we’ve compiled five real-life database examples that showcase their practical applications. Each example highlights a specific use case, from customer management to workflow automation, demonstrating how databases help businesses stay organized, efficient, and data-driven.
Whether you’re a small business owner or part of a larger organization, these examples will show how a well-structured database can improve decision-making, save time, and even unlock new opportunities.
What Is a Database?
A database is an organized way of storing information so it can be easily accessed, managed, and updated. Think of it as a digital filing system where you can keep records—like customer details, sales data, inventory lists, or employee information—in one place. Databases make it easier to find, analyze, and share data, enabling businesses and organizations to operate more efficiently.
Database vs Spreadsheet
Unlike a spreadsheet, a database is designed to handle large and complex datasets without slowing down or becoming disorganized. It allows multiple users to access and update data simultaneously while maintaining accuracy and consistency.
Additionally, databases provide tools for querying and reporting, making it easy to extract insights and automate tasks, which is difficult to achieve with a basic spreadsheet.
For example, if you run a retail store, a database can help you track products, monitor stock levels, and manage supplier details. Unlike a spreadsheet, which might become unwieldy as your business grows, a database allows you to handle larger volumes of data, maintain accuracy, and create tailored reports to guide your decisions.
Whether it’s keeping customer records in order or managing a workflow, databases are essential tools for staying organized and making data-driven decisions.
5 Real-Life Database Examples
Here are five common database examples that are widely used in real-world businesses. These databases help manage customer information, inventory, suppliers, HR records, and accounting data.
1. Customer Database
A customer database is a centralized system used to store, manage, and organize information about a business’s customers. It typically includes details such as contact information, purchase history, preferences, and interactions. It helps businesses improve customer relationships and make data-driven decisions.
By using a customer database, businesses can store and organize customer data systematically. They can also make the data easily accessible for various purposes such as marketing, sales, and customer service.
By maintaining a comprehensive customer database, businesses can gain insights into their customer base. This enables them to tailor their products, services, and communications to meet customers’ needs and preferences.
In essence, a customer database serves as the backbone of effective customer relationship management. That’s why customer databases are also sometimes referred to as customer relationship management or CRM systems.
Customer Database Template
Ready to build your own customer database? Follow this simple 3-step guide to get started with creating a professional and efficient solution tailored to your needs.
Customer Database Schema
Below is a customer database schema that outlines how you can structure and store key information about your customers, including personal details, purchase history, and preferences. This schema serves as a foundation for creating a well-organized and efficient customer database that you can customize to meet your specific business needs.
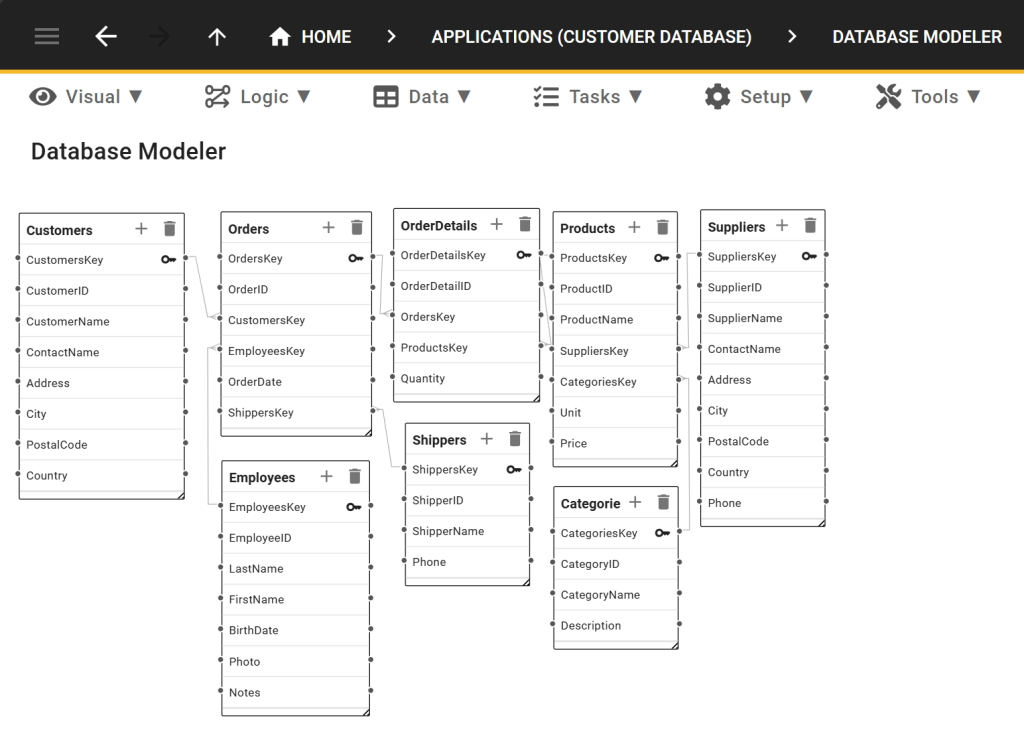
2. Inventory Database
An inventory database is a specialized system designed to store and manage detailed information about the items in your inventory and another popular real-life database example.
At its simplest, it tracks basic details like item names and quantities. For businesses with more complex needs, an inventory database can expand to include a wide range of attributes, such as product dimensions, weight, color, material, size, country of origin, or packaging specifications.
The true value of an inventory database lies in its functionality as a centralized and searchable resource. It enables businesses to efficiently manage stock levels, monitor item details, and ensure accurate tracking. This makes it a critical tool for maintaining operational efficiency, optimizing inventory levels, and improving decision-making.
Inventory Database Template
Ready to build your own inventory database? Follow this simple 3-step guide to get started with creating a professional and efficient solution tailored to your needs.
3. HR Database
Unless you are a solo entrepreneur, managing employee information is a critical aspect of running a business. An HR database serves as a centralized system to store, organize, and access key details about your workforce. From basic information such as names, contact details, and job titles to more complex data like employment history, benefits, certifications, and performance reviews, an HR database consolidates everything in one accessible place.
This database helps streamline HR processes, ensuring compliance, supporting workforce planning, and providing insights for decision-making. Whether tracking leave balances, managing payroll details, or monitoring training progress, an HR database is an essential tool for efficient employee management and fostering a productive workplace.
HR Database Template
Ready to build your own HR database? Follow this simple 3-step guide to get started with creating a professional and efficient solution tailored to your HR needs.
4. Supplier Database
A supplier database is a centralized system to store and manage vital information about your vendors. This can include fundamental details like supplier names, contact information, contract terms, and pricing agreements, as well as operational specifics such as delivery schedules, minimum order quantities, and payment terms.
Depending on your industry, a supplier database can also track specialized attributes, such as compliance certifications (e.g., ISO-certified, fair trade), product quality ratings, and lead times. It may also flag strategic partnerships or agreements, like “exclusive supplier” or “preferred vendor” status.
By maintaining this information in a searchable database, businesses can efficiently evaluate supplier performance, ensure compliance, and build more reliable supply chains.
Supplier Database Template
Ready to build your own supplier database? Follow this simple 3-step guide to get started with creating a professional and efficient solution tailored to your supplier management needs.
5. Accounting Database
An accounting database is used to manage financial transactions, records, and reports for a business. It stores crucial data such as income, expenses, invoices, payroll, and balance sheets, enabling businesses to maintain an accurate and up-to-date financial overview.
For small businesses or larger enterprises, an accounting database helps automate processes like invoicing, expense tracking, and tax calculations, ensuring compliance and financial transparency. By centralizing all financial data, it also simplifies auditing, improves accuracy, and helps businesses make more informed financial decisions. Additionally, accounting databases can integrate with other systems, such as banking or inventory management, to streamline operations.
Accounting Database Template
Ready to build your own accounting database? Follow this simple 3-step guide to get started with creating a professional and efficient solution tailored to your accounting needs.
Build Your Own Database Application
These 5 real-world database examples illustrate the importance of databases in business management and day-to-day operations. Almost every aspect of business is better managed with a custom database in place.
To create your own database, try Five. With Five’s low-code platform, you can rapidly design and deploy custom database applications tailored to your business needs – without needing to write extensive code.
Whether you’re building a customer, HR, or inventory database, Five’s intuitive tools make it easy to set up databases, design forms, generate reports, and even create custom dashboards. Plus, its user-friendly interface allows you to manage your data and workflows seamlessly.
Get started with Five today and take the first step towards building a custom database application that works perfectly for your business.
Five has a team of experts ready to assist you with your database development. So, if you ever feel like you’re in over your head, don’t worry, our expert developers are here to help. And yes, we promise not to charge you an arm and a leg or leave you with a system that only we understand.
To get a free consultation, visit this page: “Hire An Expert.”


